LPN Training: A Comprehensive Guide to Opening the Door to a Nursing Career
With the rapid development of the US medical industry, the demand for nursing staff continues to rise. Licensed Practical Nurse (LPN) is an indispensable member of the medical team, responsible for basic nursing, patient monitoring and medical support. For those who want to enter the nursing industry and quickly obtain professional qualifications, LPN training provides a systematic learning path and practice opportunities. This article will introduce the content, process, examination requirements and career prospects of LPN training in detail, and combine real cases to help readers fully understand the necessary path to becoming an LPN.

1. What is LPN training?
LPN training refers to the process of learning basic nursing knowledge and skills through a certified vocational nursing education program. The training content covers anatomy, physiology, pharmacology, nursing theory, clinical skills and patient communication. The training aims to cultivate professionals who are capable of providing safe and effective care and are competent in nursing work in hospitals, nursing homes, clinics and community medical institutions.
Most LPN training programs are offered by community colleges, vocational schools or nursing schools. The courses usually last about 12 months. Some programs can be completed within 7 months, while others may take up to two years. The specific duration depends on the learning progress and course settings.
2. Main course content of LPN training
Basic nursing knowledge
Includes nursing ethics, professional responsibility, patient safety, infection control and basic nursing techniques, such as measuring vital signs, wound care and assisting with daily living activities.
Anatomy and physiology
Systematically study the structure and function of the human body, understand the normal operation and disease state of each system, and provide a scientific basis for clinical nursing.
Pharmacology
Master the classification, mechanism of action, route of administration and side effects of commonly used drugs to ensure safe medication and patient education.
Clinical skills training
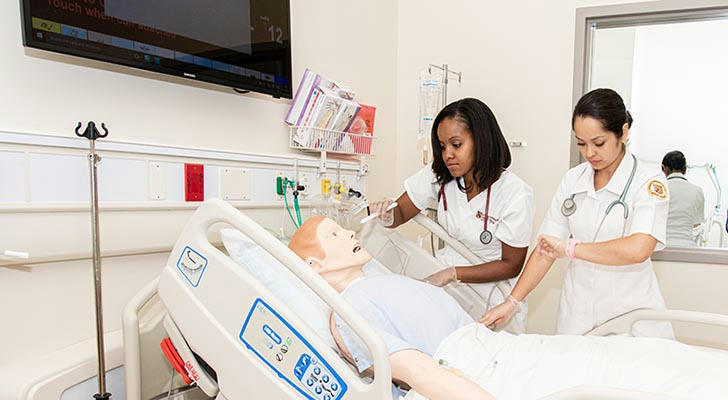
Through simulation and actual clinical internships, learn operation skills such as injection, catheterization, intravenous infusion, and first aid treatment to improve hands-on ability and emergency response.
Patient communication and psychological care
Cultivate good communication skills, understand the psychological needs of patients, and provide emotional support and health guidance.
3. Admission requirements and process for LPN training
Admission requirements
Graduate from high school or hold a GED certificate.
Pass background check and drug screening.
Some programs require a minimum GPA or completion of basic science courses.
Have a valid CPR certificate.
Registration and application
Choose a training program approved by a national nursing education accreditation agency (such as ACEN), submit application materials, and participate in an interview or entrance examination (depending on the specific program).
Training and learning
Complete theoretical courses and clinical internships, usually including 500 to 700 hours of clinical practice, to ensure that students have practical work capabilities.
Pass the NCLEX-PN exam
After the training, students need to apply for the National Licensed Practical Nursing Examination (NCLEX-PN), which covers four major areas: physiological integrity, safe nursing environment, health promotion, and psychosocial integrity. Only after passing the exam can you obtain a license to practice issued by the state nursing board.
4. Career development path after LPN training
After becoming an LPN, career development is diverse:
Work in hospitals, long-term care institutions, clinics, home care and other environments, and undertake basic nursing and patient monitoring tasks.
Obtain specialist certification through experience accumulation and continuing education, such as elderly care, wound care or chronic disease management.
Choose to participate in the LPN-to-RN bridge program to further improve academic qualifications and career levels and become a registered nurse (RN).
Some LPNs turn to related fields such as medical management, health education or medical sales.
5. Real case sharing
Case 1: Emily's path to realize her nursing dream

After graduating from high school, Emily chose to participate in the LPN training program of the local community college. After a year of intensive study and clinical internship, she successfully passed the NCLEX-PN exam and obtained the qualification of a licensed nurse. After joining a nursing home, Emily was not only competent for daily nursing work, but also actively participated in patient health education. Two years later, she successfully became a registered nurse through the LPN-to-RN bridge course, and her career development space was greatly expanded.
Case 2: Michael's career transition
Michael was originally a manufacturing worker, but turned to the nursing industry due to work needs and interests. Through the accelerated LPN training program, he completed the course and passed the license exam in just 8 months. With solid nursing skills and good communication skills, Michael quickly adapted to the hospital environment and gained recognition from colleagues and patients. In the future, he plans to continue his studies to improve his nursing professional level.
6. Advantages and challenges of LPN training
Advantages:
The training cycle is relatively short, usually about 1 year, which is suitable for people who want to quickly enter the nursing industry.
The admission threshold is relatively low, suitable for students from a variety of backgrounds.
There is a strong demand for the profession, abundant job opportunities, and stable salaries.
Provide solid clinical practice experience to enhance employment competitiveness.
Challenges:
The training content is intensive, theory and practice are closely combined, and a high degree of self-discipline and commitment are required.
Clinical internships may face high-intensity work environments and emotional pressure.
It is necessary to pass a strict national license examination, and the preparation pressure is relatively high.

Conclusion
LPN training provides a practical career path for people who are interested in the nursing industry. Through systematic theoretical learning and rich clinical practice, the training not only helps students master basic nursing skills, but also lays a solid foundation for subsequent career development. Real cases show that LPN training can help students from different backgrounds achieve career transformation and advancement. Faced with the continued growth of nursing needs in the medical industry, choosing LPN training is an important step to enter the nursing field and realize your career dream.
